What are off-target effects and why are concerning?
Off-target CRISPR effects are unintended editing events that occur at untargeted sites in the genome that are genetically similar to the targeted site. A large number of studies have reported that there can occur in CRISPR edited plants. Therefore, it is necessary to detect the off-target mutatuin in transgenic plants. And for different CRISPR systems, this kind of off-target usually exists at the level of DNA and RNA.
How to do?
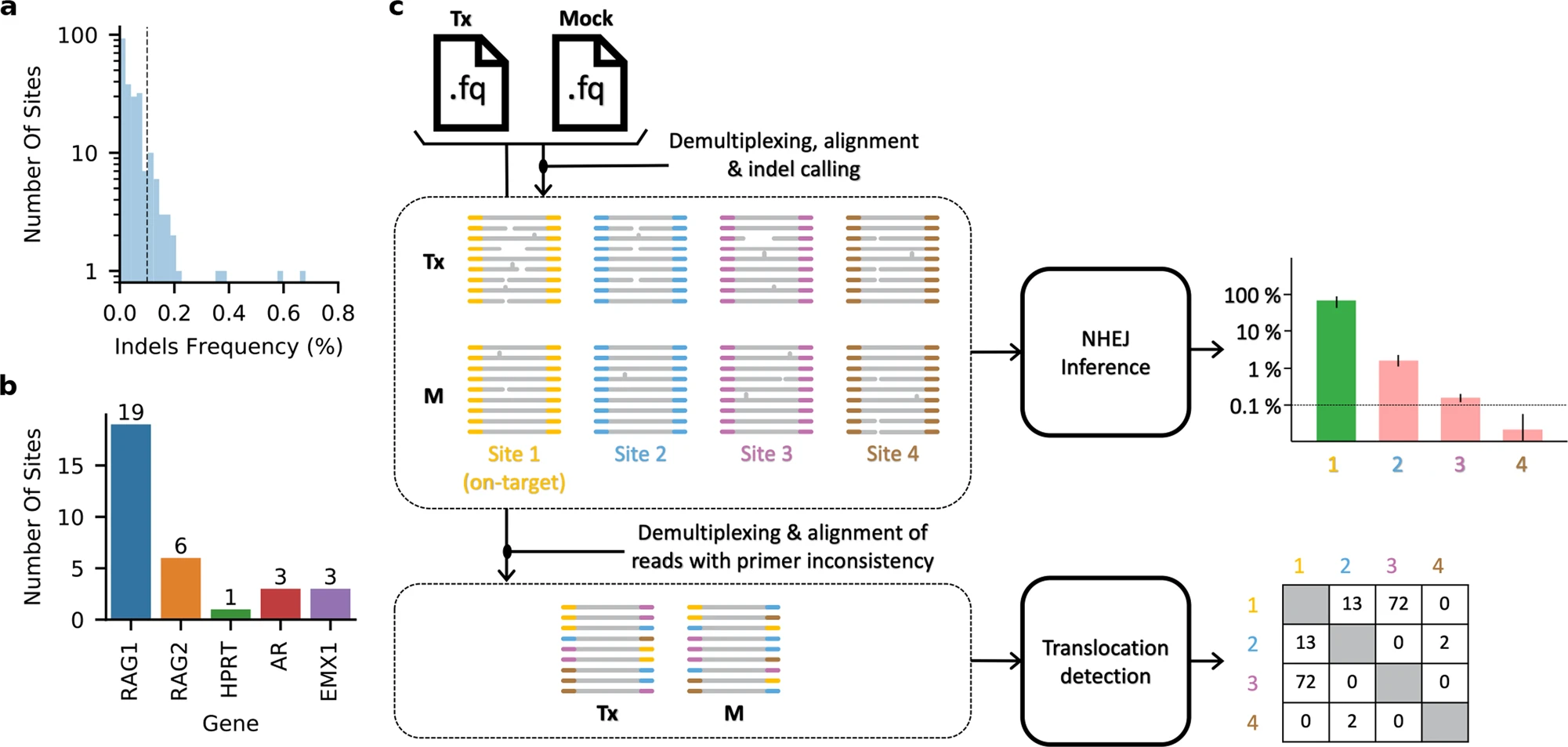
The whole genome DNA and transcriptome of transgenic lines and controls were sequenced. Reference genome alignment and SNV call were carried out, and then the genome distribution of SNV was counted. A workflow of these steps is in here.
DNA levels
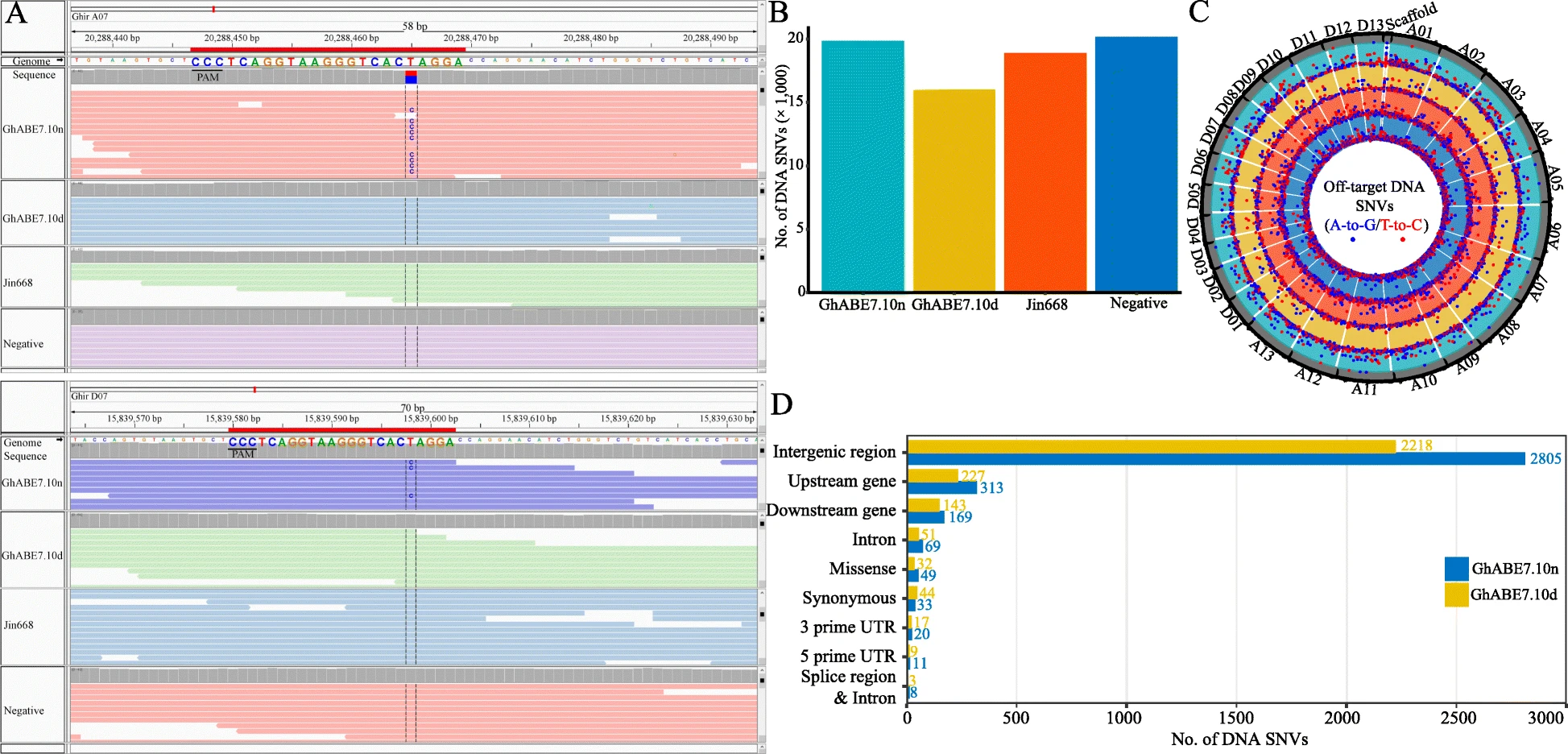
Detection of off-target mutations at DNA levels by WGS
Genomic DNA was extracted from young leaves of an individual cotton plant (transgenic, negative (undergone tissue culture and plant regeneration but without T-DNA insertion) and WT) using the Plant Genomic DNA Kit (Tiangen Biotech, China). A total of four plants, including one WT plant, one negative plant, and two base editor plants, edited by GhABE7.10-nCas9 and GhABE7.10-dCas9 with two pairs of sgRNAs for GhPEBP (tRNA-sgRNA1-tRNA-sgRNA2) gene, were used to evaluate genome-wide genetic variants. For each plant, ca. 1.5 μg genomic DNA was prepared to generate a standard Illumina short-read genomic library and paired-end sequencing (2 × 150 bp) on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencer in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations (Illumina, San Diego, CA), ultimately resulting in more than 1 Tb raw reads (the average depth being 50×). The filtered (Trimmomatic) and quality-checked (FastQC) clean reads were mapped to the reference-grade Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1 genome (http://cotton.hzau.edu.cn/EN/download.php) with BWA (v0.7.17). Samtools (v1.9) was used to filter multiple mapping reads and sort BAM files by read name. The picard program (v2.1.1) (http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/) was used to mark duplicative reads, and the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK v4.1), Sentieon (201911) (https://www.sentieon.com/), and LoFreq (v2.1.5) were employed to variant calling. The high-confidence SNVs, which had to be identified by all three software and filtered with parameters “QD < 2.0 || FS > 60.0 || MQ < 40.0 || MQRankSum < -12.5 || ReadPosRankSum < -8.0,” were used for subsequent analysis.
Off-target sites were predicted by Cas-OFFinder (v2.4), allowing up to 5-nt mismatches. SnpEff was used to annotation and predicts the effects of each off-target variant based on Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1 genome.
The Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) was used to check obtained SNVs.
RNA levels
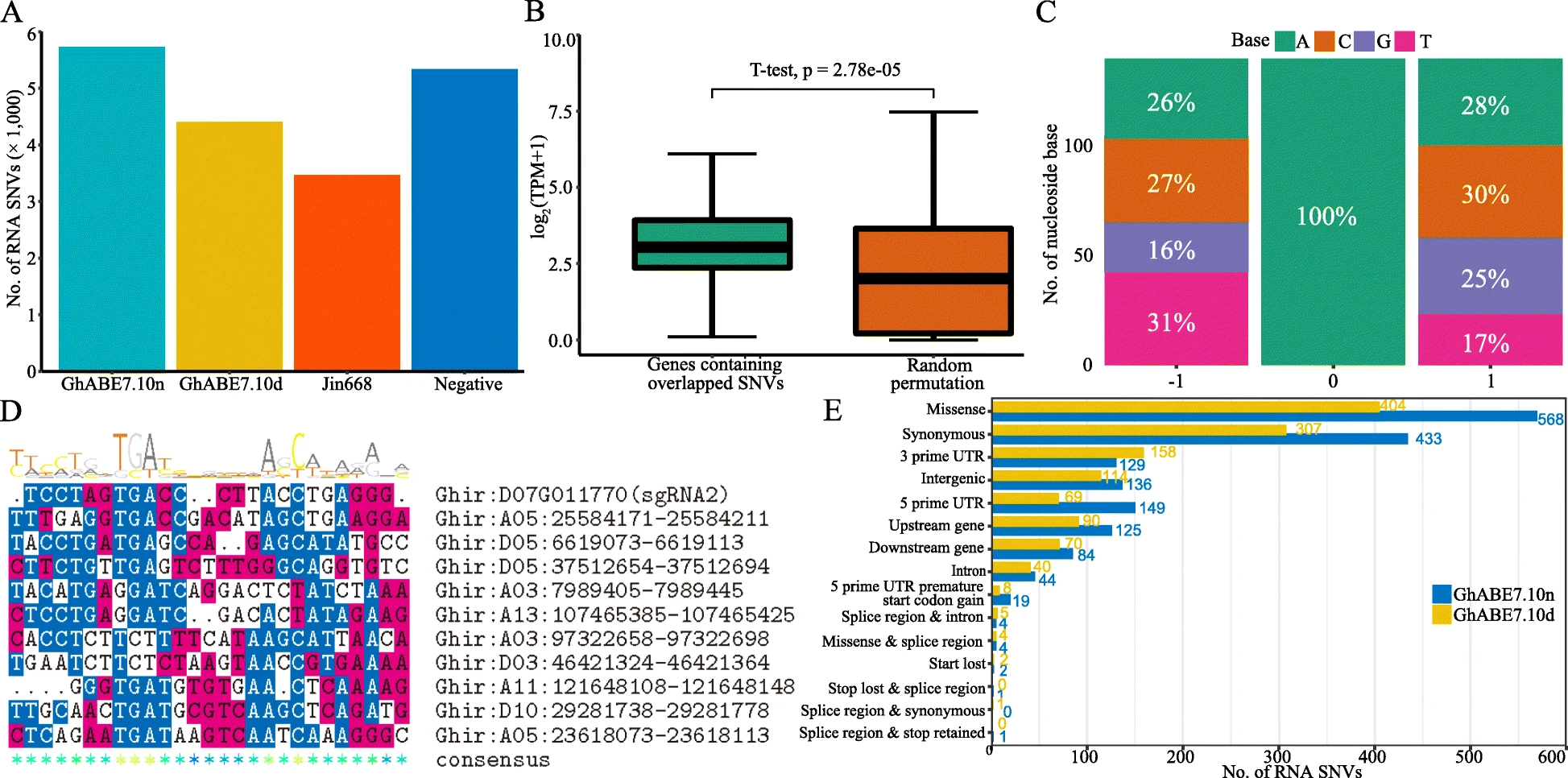
Detection of off-target mutations in RNA sequence
The samples from individual plants that were used to detect off-target genomic mutations were also prepared for RNA-editing analysis. The total RNA of four plants described above was isolated as previously described. For library construction, mRNAs were fragmented and converted to cDNA using oligo (dT) primers (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). High-throughput mRNA sequencing was carried out using the Illumina Hiseq platform according to the manufacturer’s recommended protocol. We generated an average of 50× paired-end reads for each sample. Illumina paired-end reads were processed as previously described. In brief, FastQC (v.0.11.8) and Trimmomatic (v.0.36) were used for quality control. Qualified reads were mapped to the reference genome Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1 genome (http://cotton.hzau.edu.cn/EN/download.php) using STAR (v.2.7.1a) in two-pass mode. Picard tools (v.2.9.2) was then applied to sort and mark duplicates of the mapped BAM files. RNA base editing variants were called using GATK (v4.1) and Sentieon (201911) (https://www.sentieon.com/) from the refined BAM files. High-confidence SNVs were identified using both software. To identify variants with high confidence, we filtered variants with parameters “QD < 2.0 || FS > 60.0 || MQ < 40.0 || MQRankSum < -12.5 || ReadPosRankSum < -8.0” and clusters of at least five SNVs that were within a window of 35 bases. The sum of mutations A-to-G and T-to-C were counted as edited as previously described.
SnpEff was also used to annotate and predict the effects of each off-target variant as for the above WGS analysis.
The 20-bp sequences adjacent to off-target RNA-SNVs (containing NGG PAM in downstream region) were extracted from the Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1 genome and aligned using the R package msa.
How do I identify CRISPR editing off-target sites?
Clone the software of DNA-seq-gatk-variant-calling and RNA-seq-gatk-variant-calling , and modify the config.yaml file for editing analysis.
Then run it with command as follows:
snakemake -j 100 -s workflow/Snakefile --use-conda --cluster-config config/cluster.json --cluster "bsub -q normal -o {cluster.output} -e {cluster.error} -n {threads}"